Many traditional high-power audio amplifiers now have an output power of more than 100 watts per channel, and most of them use separate circuit components. Therefore, in order to ensure the stability of the output and sound effects, engineers usually need to spend a lot of energy to match and adjust the high-definition audio amplifier.
This article takes National Semiconductor's audio driver LME49810 as an example. This component can provide a peak-to-peak output voltage swing of 200V and can drive different types of output stages. It is suitable for high-end consumer and professional audio applications, including active recording studios. Monitors, subwoofers, audio / video receivers, commercial sound reinforcement systems, non-original audio, professional-grade mixers, distributed audio and guitar amplifiers, etc. In addition, it is also suitable for various industrial audio systems with high voltage and low distortion requirements. It can provide a more streamlined design for audio systems, help designers to develop high-performance audio systems more easily, achieve higher stability and consistency, and greatly reduce the separation and matching of separate components during system development and production.
Design tips
There are many ways to design high-quality audio systems using National Semiconductor's audio drivers. The following are design suggestions.
Input stage: The input stage design is the most critical part of the amplifier. By subtracting the signal from the feedback, the input stage will generate an error signal, and then drive this error signal to the output. The error signal is usually small enough to provide sufficient linearity for the amplifier.
LME49810 is a bipolar input amplifier, its input impedance matching is very important. Due to the bias current from the positive input port and the negative input port, the input impedance mismatch will cause the input offset voltage. The input offset voltage will be amplified according to the infinite loop gain. Of course, the input bias current of the LME49810 is very low, and for general applications, the offset voltage that appears at the output can be ignored.
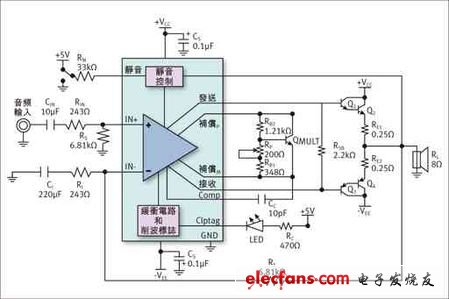
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of input stage and feedback application
In general, there are two types of audio input designs commonly used: AC or DC coupled input. The advantage of AC-coupled input is that the input DC offset of the amplifier from the preamplifier, filter stage or codec stage is generally zero, and there is no need to add any DC servo circuit in the amplifier to prevent DC failure. The advantage of DC-coupled input is that it does not require the use of large-sized and expensive AC-coupling capacitors; low-frequency distortion caused by AC-coupling capacitors does not occur; and the noise of AC-coupled RC networks can be reduced.
Negative feedback coefficient: The negative feedback setting of the power amplifier can bring higher stability and linearity to the system. The phase shift occurs when the amplifier is operating at high frequencies, and a large negative feedback coefficient can reduce instability and oscillation at high frequencies. In split amplifier systems, high feedback coefficients will cause poor transient response or high frequency instability. However, LME49810 has a higher open-loop gain, so its dead-loop gain error and power supply ripple suppression will be smaller, which can maximize the negative feedback in the circuit, thus improving the linearity of the system. Generally, a voltage gain of 30dB to 40dB is recommended.
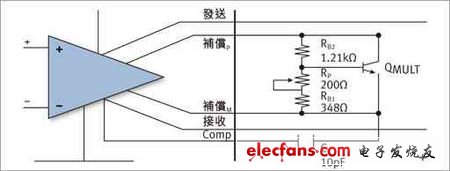
Figure 2: Output bias circuit structure
Compensation: The amplifier's compensation is used to adjust the open-loop gain and phase performance so that the system can be stabilized when feedback is turned off. Generally speaking, the higher the stability compensation, the better. However, the greater the compensation, the lower the bandwidth and slew rate of the audio chip. A lower slew rate will cause the system to produce softer audio characteristics. Conversely, a higher slew rate will produce a clearer and True audio characteristics. LME49810 Miller compensation is achieved by inserting a capacitor between the 'Comp' and 'BiasM' pins. The most suitable capacitor value range is 10p to 100p. In addition, the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of the compensation capacitor should be low to avoid potential zeros caused by the equivalent series resistance of the capacitor. In general, ceramic capacitors are better than electrolytic capacitors.
Mute: The MUTE pin is controlled by the amount of current flowing in. From 50uA to 100uA is the 'PLAY' mode, and below 50uA is the 'MUTE' mode. It is recommended not to let the current flowing into the MUTE pin exceed 200uA.
Output bias: LME49810 has two dedicated pins (BIASP and BIASM) for setting bias, which can provide a certain output bias current. The variable resistor Rpot can be used to adjust the bias current of the output stage. Lowering the resistance of Rpot + R b1 can increase the bias voltage. The multiplier QMULT is used to compensate the bias voltage to prevent thermal drift of the bipolar output transistor. QMULT must be connected to the same heat sink as the output transistor.
Output transistor: The most common output stage in an audio power amplifier is the emitter follower shown in Figure 3. It is often referred to as a dual-emitter follower or Darlington tube. The first follower will be the driver of the output stage.

Figure 3: Output shot follower â–
Usb-C To Lightning Cables,Pd Charger Cable,Fireproof Braided Charger Cable,Pd Fast Charger Cable For Apple Devices
Dongguan Pinji Electronic Technology Limited , https://www.iquaxusb4cable.com
