The drone remote controller is a crucial device that allows users to operate and control the drone effectively. As drones have evolved over time, so have their remote controls, with continuous improvements aimed at making the flying experience more intuitive and user-friendly. These enhancements focus on simplifying the control process, ensuring that even beginners can easily manage and enjoy flying their drones.
To better understand the differences between traditional UAV remote controllers and the newer "Black Technology" models, we’ll start by exploring the basics of conventional remote controls. This will help newcomers—often referred to as "Little Whites"—get a clearer picture of how these devices work.
**First, Understanding Traditional Drone Remote Controllers**
A typical remote controller includes basic components such as switches, buttons, and an antenna. While the layout and number of buttons may vary depending on the drone’s specific functions, the core structure remains similar across most models. The design usually features joysticks for flight control, along with various function keys for camera adjustments, mode switching, and other operational tasks.
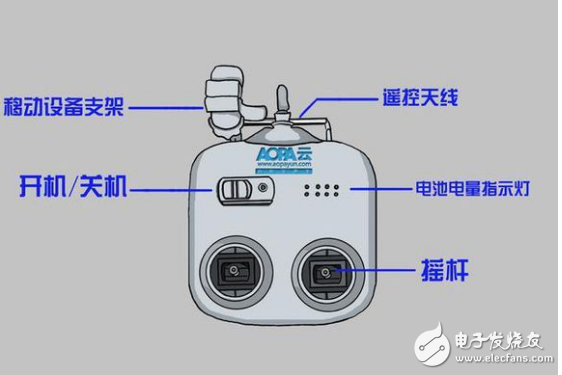
**Understanding the Structure of UAV Remote Controls**
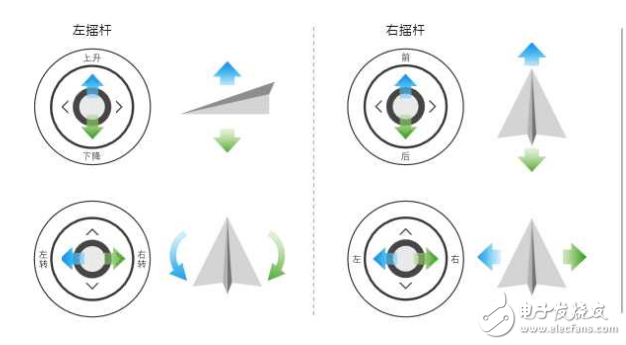
You might have heard terms like "American hand," "Japanese hand," or "Chinese hand." These refer to different joystick configurations used in remote controls. The main difference lies in how the controls are arranged—specifically, which side of the controller is used for throttle and yaw movements.
So, what exactly is a "channel"? A channel represents a separate control input that the remote uses to communicate with the drone. For example, a four-channel remote typically controls the drone's up/down, left/right, forward/backward, and rotation. Most modern drones require at least four channels for stable and precise flight.
**Function Overview of a Four-Rotor UAV Remote Control**
Many drone enthusiasts enjoy assembling their own drones and learning how to fly them. Before taking off, it's essential to understand the functions of the remote control. Let’s take a closer look at a standard four-rotor drone remote control and its key features.

[1] **Video Recording Button**: Press once to start recording video, press again to stop.
[2] **PTZ Angle Control Wheel**: Slide left or right to adjust the camera’s vertical angle.
[3] **Mode Switching Function**: This button lets you switch between different flight modes. The P (Positioning) mode is ideal for beginners, offering GPS or visual-based stabilization. It has three sub-modes:
- **P-GPS**: Uses GPS for precise hovering.
- **P-OPTI**: Uses visual positioning when GPS is weak or unavailable.
- **P-ATTI**: Provides only attitude stabilization without positioning.
**A Mode (Attitude)**: No GPS or visual positioning, just basic stabilization. Good for returning home if GPS is strong.
**F Mode (Function)**: Uses GPS for hovering and enables intelligent heading control.
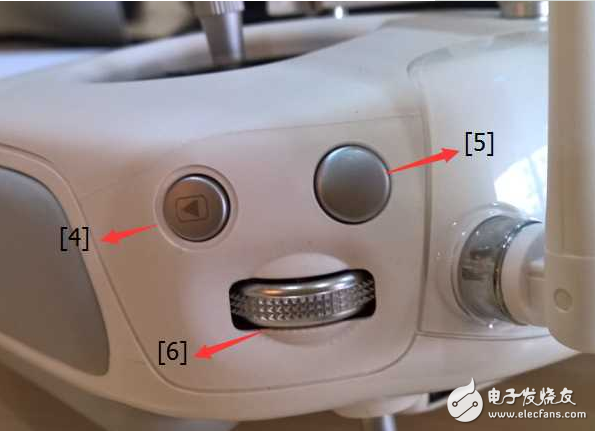
[4] **Playback Button**: Short press to play back media through the drone app; press again to return to photo/video mode.
[5] **Photo Button**: Press to take a photo.
[6] **Camera Settings**: Adjust camera parameters and flip photos/videos using the playback button.

[7] & [8] **Left and Right Joysticks**: These are used for controlling the drone’s movement. In the default US hand configuration, the left stick controls throttle and yaw, while the right stick manages pitch and roll.
[9] **Power Button**: Short press to check battery level; long press to turn on the remote and connect to the drone.
[10] **Intelligent Return Button**: Hold until you hear a beep to activate the return-to-home function. The drone will automatically fly back to the last recorded position. You can still manually control it during the return. A short press initiates the return, and you regain full control after that.
AL/CU Universal Terminal Block
Cable Terminal Block,Universal Terminal Block,Waterproof Terminal Block,Low Voltage Terminal Block
ZHEJIANG QIANNA ELECTRIC CO.,LTD , https://www.traner-elec.com
