This paper presents a multi-serial communication programming approach under the embedded real-time operating system μC/OS-II, using the LPC2365 as the core processor. For fixed-length short-byte frame data, the reception task is accomplished by setting an appropriate byte trigger depth. For variable-length long-byte frame data, the task is completed through one interrupt and a waiting delay. Additionally, for handling large volumes of data, a FIFO (First In, First Out) data queue method is implemented to ensure efficient data management.
These techniques effectively support the communication tasks involving multiple serial ports with high data volume. When a domestically-made sea-going high-altitude hardware target is being towed, it must transmit various parameters in real time to the towing master via a wireless link, while also receiving remote control commands to perform specific actions. The parameters include switch control status, battery voltage, radio altimeter reading, flight height setting, vertical acceleration, rudder angle, temperature, GPS receiver output values, and more.
The first seven parameters are collected by a data acquisition board, assembled into frame data, and transmitted via RS232 at 9600 bps and 1 Hz. The data frame size is fixed at 12 bytes, while remote command data is received at 6 bytes per frame. The general-purpose GPS receiver outputs two statements—$GPGGA and $GPRMC—at 9600 bps and 1 Hz, with a variable number of bytes, typically not exceeding 160. The high-performance GPS operates at 57,600 bps and 20 Hz, outputting nine parameters such as RT, RD, TO, SI, RC, CP, DC, FC, and PV, with a total data size generally under 305 bytes.
To meet the requirement of uploading 75 bytes of data per frame (with three identical frames returned if a remote command is received), the system uploads data to the towing master at a rate of one frame per second for real-time display. The high-performance GPS data is directly uploaded to the towed master's storage for post-processing, highlighting the need for a robust multi-serial communication solution in this application.
1 Working Principle
An ARM7-based LPC2365 processor with multiple serial ports is used to receive real-time data from the data acquisition board and the general-purpose GPS receiver. After framing, the data is stored in a FIFO transmission queue using a mutual exclusion semaphore. High-performance GPS data is also stored in the same queue. When the queue is not empty, a binary semaphore triggers the serial port transmission task until one frame is fully sent. A schematic of the data flow is shown in Figure 1.
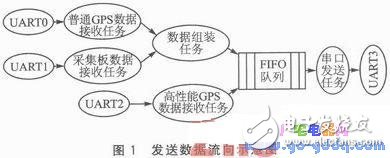
The application is developed on μC/OS-II, creating separate tasks for receiving, sending, and framing data across different serial ports.
2 Hardware Design
The main control CPU uses NXP’s ARM7 LPC2365, featuring 256 KB Flash, 32 KB SRAM, four full-duplex UARTs, and up to 70 general-purpose I/Os. These rich resources allow the device to communicate with the data acquisition board, general-purpose GPS, high-performance GPS, and a digital transmission module. The Flash and SRAM are sufficient to run μC/OS-II and its applications.
Given that the high-performance GPS transmits at 57,600 bps, 20 Hz, and 305 bytes per frame, the data duty cycle reaches 85%. To handle this and other parameter data, a high-speed digital transmission module is essential for reliable communication.
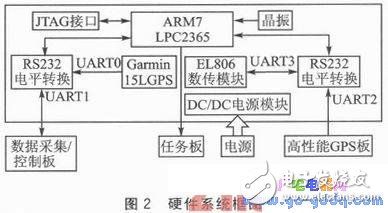
The GE MDS EL806 digital transmission module offers advanced frequency-modulated spread spectrum technology, providing industrial-grade wireless communication at up to 115,200 bps in the 902–928 MHz band. It excels in reliability, error correction, and data integrity, along with low power consumption (up to 1 W) and strong environmental adaptability. The hardware block diagram is shown in Figure 2.
3 Software Design
3.1 μC/OS-II Porting
μC/OS-II is a portable, scalable, and open-source real-time multitasking kernel suitable for various microprocessors, including 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit architectures. To run it on custom hardware, the OS must be ported to the specific CPU architecture. While there are many resources available, a practical approach is to download pre-transplanted routines for ARM7, simplifying the process significantly.
3.2 Application Programming
P04 Series Push Wire Connectors
compact universal lever connector, perfect for tight spaces
transparent housing for visual inspection of connection
reusable
Lever-nuts,Transparent Enclosure Terminal Blocks,wire harness connectors,compact splicing connector,cage clamp connector
Jiangmen Krealux Electrical Appliances Co.,Ltd. , https://www.krealux-online.com
