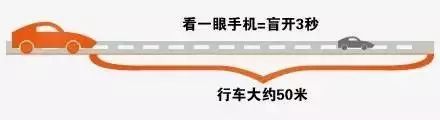
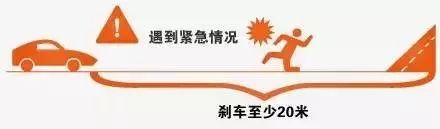
During driving, it's common for drivers to glance at the dashboard to check speed, fuel levels, and other critical information. These quick glances typically last between 1 and 3 seconds. At an average urban speed of 65 km/h, this brief distraction can mean driving about 54 meters with your eyes off the road—equivalent to driving blindfolded for that distance. In reality, countless traffic accidents are caused by such distractions, highlighting the need for safer alternatives.
While it’s impossible to avoid checking the dashboard entirely, you don’t have to look down. That’s where HUD technology comes in. Head-Up Display (HUD) is a groundbreaking innovation designed to enhance driver safety by projecting essential driving information directly into the driver’s field of view, keeping their attention on the road.
The concept of HUD originated in military aviation, where pilots needed to access critical flight data without constantly looking down at their instruments. By using optical projection, early HUD systems allowed pilots to see vital information, like speed and altitude, while maintaining focus on the sky. This principle was later adapted for automotive use, aiming to reduce driver distraction and improve safety on the road.

Since the 1980s, HUD has evolved from being a niche feature to a more mainstream technology. With the rise of augmented reality and smart devices like Google Glass, HUD has gained even more attention. It’s often described as “smart glasses for cars,†offering a seamless way to display driving data, navigation, and even messages without requiring the driver to take their eyes off the road.
Initially, HUD focused on basic driving metrics like speed and fuel level. But as technology advanced, it began incorporating more complex functions, including real-time navigation, incoming calls, and even interactive features. The goal was to make the car a mobile hub, integrating all necessary information into a single, intuitive display.

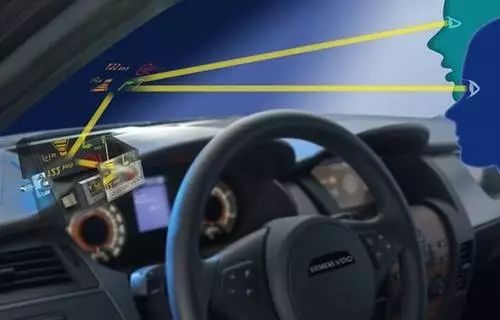
How does HUD work? Essentially, it uses a projector to cast images onto the windshield. A mirror reflects the image, making it appear as if it’s floating several meters ahead of the driver. This design allows the driver to read the information without shifting their gaze too far from the road, reducing eye strain and improving reaction times.
The position of the HUD image on the windshield is adjustable, depending on the driver’s needs. This is achieved through precise adjustments of the projector and mirrors. Additionally, because windshields are curved, special optical designs are used to ensure the image remains clear and undistorted.
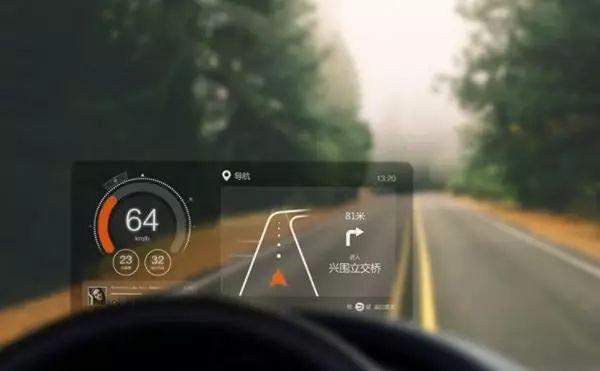
Today, HUD systems can display a wide range of information, including speed, navigation directions, warnings, and even vehicle diagnostics. They help drivers stay informed without constantly looking away from the road, significantly enhancing safety during daily commutes or long trips.

With advancements in technology, modern HUDs now support high-precision navigation, real-time traffic updates, and even smartphone integration. Imagine being able to receive text messages or make calls without taking your hands off the wheel—this is the future of driving with HUD technology.
One of the most significant benefits of HUD is its ability to reduce visual distractions. Instead of looking down at the dashboard, drivers can simply glance up to see important information. This not only improves safety but also enhances the overall driving experience.
Currently, there are three main types of HUD implementations: direct windshield projection, additional displays, and mobile phone-based solutions. While each has its own advantages, they also come with limitations, especially when it comes to clarity, adaptability, and performance under different lighting conditions.
Looking ahead, the future of HUD technology is promising. Innovations like 3D HUDs, enhanced augmented reality features, and deeper integration with autonomous driving systems are expected to redefine how we interact with our vehicles. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, HUD will play a crucial role in shaping the next generation of smart, safe, and connected cars.
All black solar panels or black frame Solar Panel, power range around 400w to 460w which is higher solar panel efficiency the front black or front and back are both black.
All black solar panel data
| mono type | mono crystalline half cut cell |
| power range | 400watt to 460watt |
| dimensions | 1176*1134*30mm |
| type | monofacial type or bifacial type |
Product details and pic
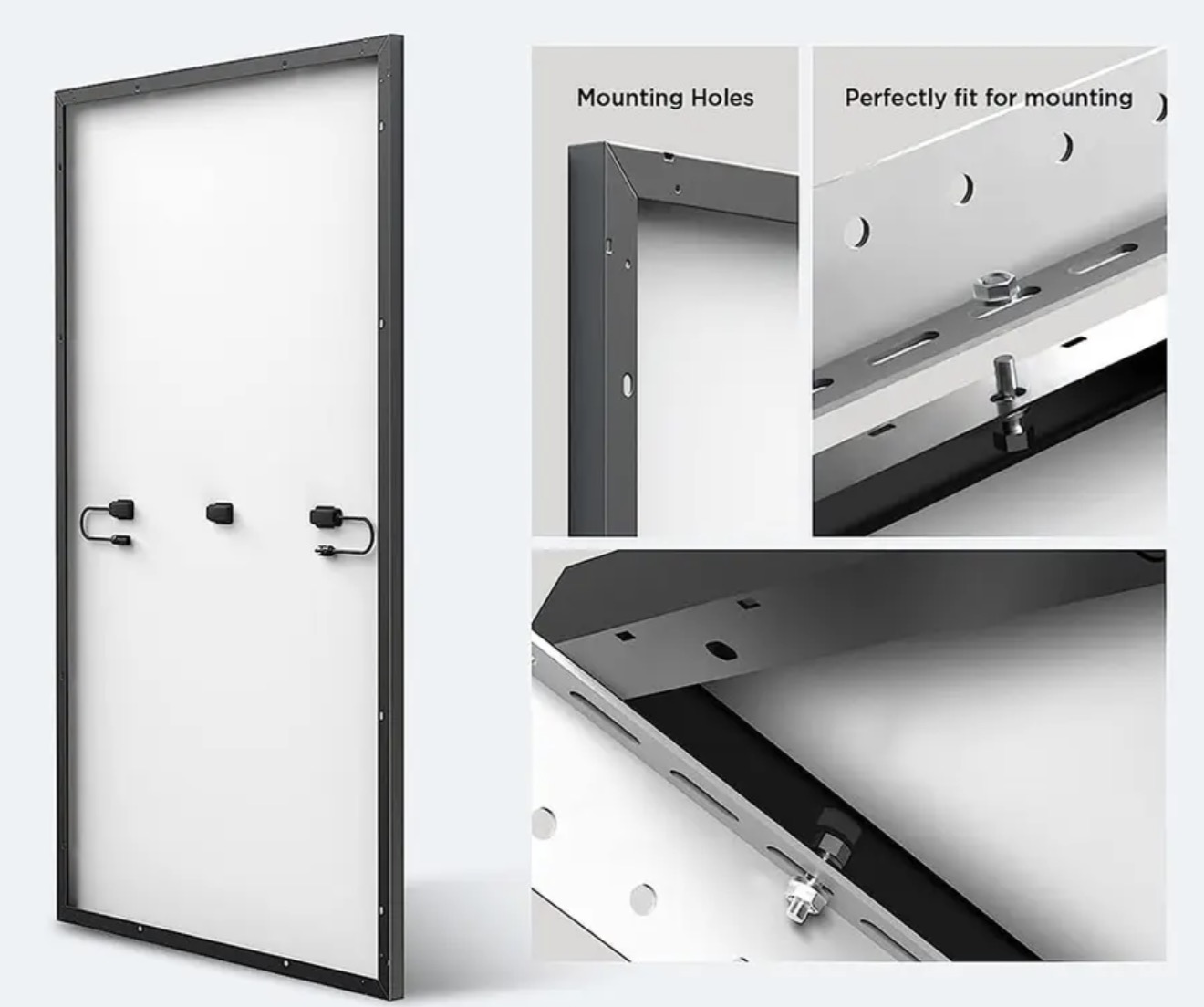


All Black Solar Panel,Trina Solar Panel Vertex S,Mono Crystalline Pv Modules,Full Black Solar Panels 420Watt
PLIER(Suzhou) Photovoltaic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pliersolar.com
