During driving, it's common for drivers to glance at the dashboard to check speed, fuel levels, and other important data. This brief action typically takes between 1 and 3 seconds. At an average urban speed of 65 km/h, this short moment away from the road equates to driving approximately 54 meters with your eyes off the road—this is a significant risk in real-life driving scenarios. Many traffic accidents are caused by driver distraction, highlighting the need for safer ways to access vehicle information while keeping focus on the road.
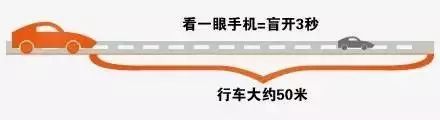
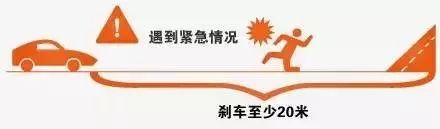
While it’s impossible to constantly watch the dashboard, it’s also not safe to look down. That’s where HUD technology comes into play. Head-Up Display (HUD) systems project essential driving information directly onto the windshield, allowing drivers to keep their eyes on the road. This innovation enhances safety and convenience, making driving more intuitive and efficient.
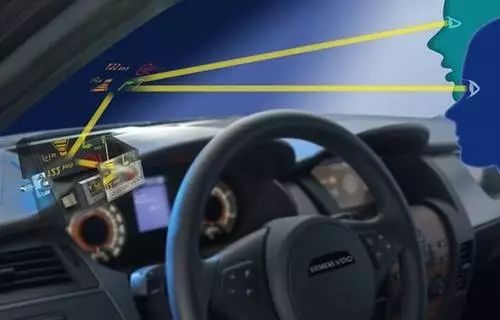
The origin of HUD technology can be traced back to military aircraft, where it was used to reduce pilot workload by displaying critical flight data without requiring them to look down. Over time, this concept transitioned to the automotive industry, aiming to improve driver safety and reduce distractions. Today, HUDs are seen as a key step toward smarter, more connected vehicles.

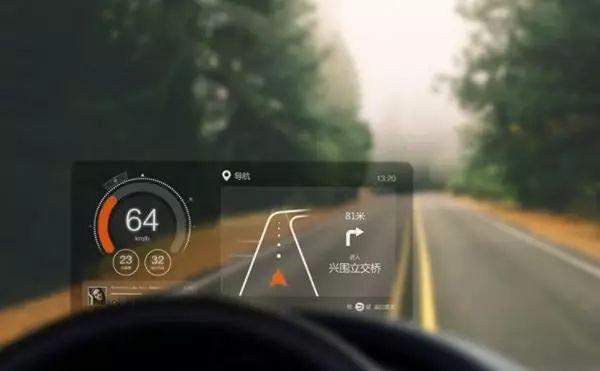
Initially, HUDs were limited to basic driving metrics like speed and fuel level. However, modern systems now integrate advanced features such as navigation, messaging, and even augmented reality. These enhancements make HUDs more than just a display—they become a central interface for driving assistance and smart connectivity.
The working principle of HUD is similar to a projector. Light from the projector is reflected off a mirror and then projected onto the windshield, creating a virtual image that appears about 2-2.5 meters ahead of the driver. This design allows the driver to view information without shifting their gaze significantly, reducing eye strain and improving reaction times.

To ensure clarity, the windshield must be specially designed. Curved windshields require precise optical adjustments to prevent image distortion. The projector and mirrors are also curved to accommodate the shape of the glass, ensuring accurate projection of information onto the windshield.
HUDs are not only useful for basic information like speed and fuel, but they also support navigation, lane guidance, and even alerts for potential hazards. By integrating these features, HUDs help drivers stay informed without compromising their attention to the road.

In addition to traditional functions, some HUDs now support smartphone integration, allowing drivers to receive messages, make calls, or even control music. This feature reduces the temptation to use a phone while driving, further enhancing safety.
One of the main advantages of HUDs is that they allow drivers to view information without looking down. This minimizes the need to adjust focus between the road and the dashboard, which can cause fatigue and slow reaction times. Studies have shown that HUDs can significantly reduce the risk of accidents caused by distracted driving.
There are several types of HUD implementations today. Some use the windshield directly, while others rely on external projectors or mobile apps. Each method has its own pros and cons, with the most advanced solutions offering high-quality, immersive displays that enhance the driving experience.

Despite its benefits, HUD technology still faces challenges. High costs, limited interaction, and lack of standardization remain barriers to widespread adoption. However, as the automotive industry continues to evolve, we can expect HUDs to become more affordable, intuitive, and integrated with future autonomous driving systems.
Looking ahead, HUDs are expected to play a crucial role in the development of intelligent and connected vehicles. With advancements in augmented reality, higher resolution, and broader field of view, the future of HUDs promises a more seamless and interactive driving experience. As car manufacturers continue to innovate, HUD technology will likely become a standard feature in many vehicles, transforming the way we drive.
All black solar panels or black frame Solar Panel, power range around 400w to 460w which is higher solar panel efficiency the front black or front and back are both black.
All black solar panel data
| mono type | mono crystalline half cut cell |
| power range | 400watt to 460watt |
| dimensions | 1176*1134*30mm |
| type | monofacial type or bifacial type |
Product details and pic
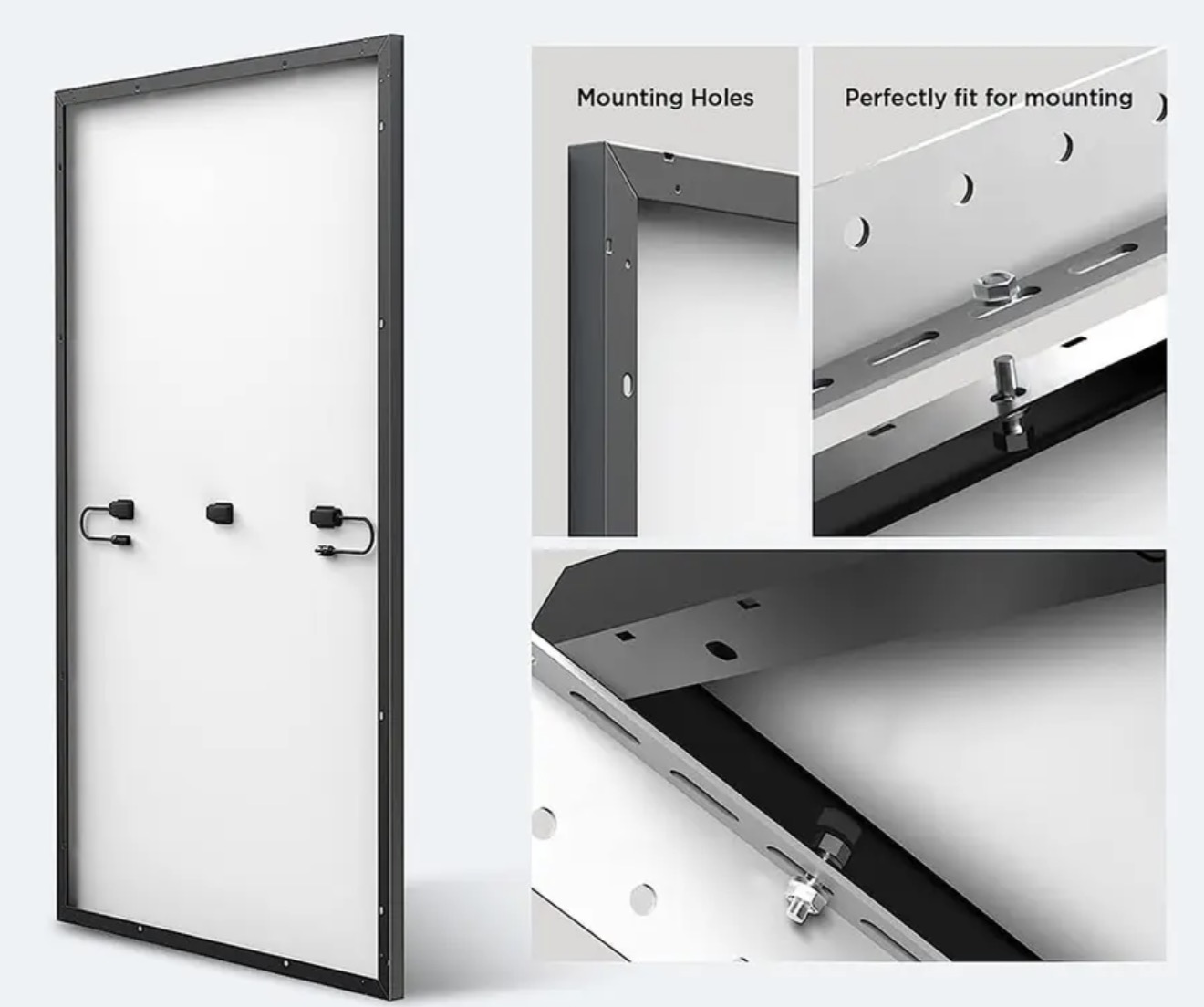


All Black Solar Panel,Trina Solar Panel Vertex S,Mono Crystalline Pv Modules,Full Black Solar Panels 420Watt
PLIER(Suzhou) Photovoltaic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pliersolar.com
