**Message Exchange Principle**
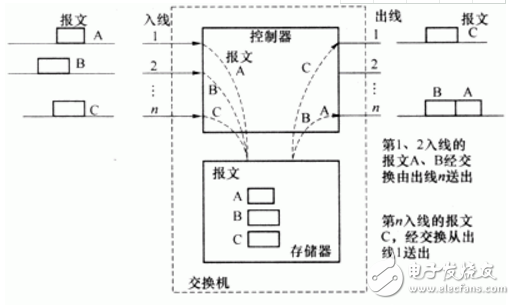
The process of message exchange involves several key steps. When a user wants to send a message, the necessary information is added to the packet header, including both the source and destination addresses. Once the packet is formed, it is sent to the switch. When the communication controller in the switch detects an incoming message on a user line, it sends an interrupt request to the central processing unit (CPU) and then transfers the message into memory word by word.
After receiving the message, the CPU processes it, such as analyzing the header, determining the route, and then transferring the message to external high-capacity memory, where it waits for an idle output line. Once a line becomes available, the message is moved from external memory to internal memory and then sent through the communication controller to the appropriate line.
**Message Exchange Characteristics**
"Store-and-forward" is a core feature of message exchange. The switch stores the entire message first and forwards it once a line is available. This method offers several benefits:
1. It avoids monopolizing the line, allowing multiple users to share one line by storing and queuing data.
2. Establishing a wireless path improves line utilization.
3. It supports multi-point transmission, where a single message can be sent to multiple users by adding an address field. Intermediate nodes then copy and forward based on that field.
4. Intermediate nodes can convert data formats, making it easier for the receiving end to handle.
5. Error detection features help avoid transmitting incorrect data.
**Message Exchange**
Message exchange is a data transmission method where packets are exchanged between systems. Each message includes information like the source and destination address, and uses store-and-forward at the switching node. This approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
**Advantages of Message Exchange**
1. No need to establish a dedicated communication line beforehand, so users can send messages anytime without connection delay.
2. Store-and-forward allows for better error handling and retransmission. Switch nodes can also choose alternative paths if a line fails, improving reliability.
3. It’s easy to implement data conversion and rate matching, enabling communication between different types of computers with varying speeds.
4. Supports multi-target delivery, meaning a single message can be sent to multiple destinations, which is difficult in circuit switching.
5. Allows priority-based transmission, ensuring critical data is processed first.
**Disadvantages of Message Exchange**
1. Because messages are stored and forwarded, there is a delay in transmission, especially under heavy network traffic. This makes it unsuitable for real-time or interactive services.
2. Only applicable to digital signals.
3. Since messages can be long, intermediate nodes must store entire messages, requiring large buffers. In some cases, messages may even be stored on disk, increasing delays.
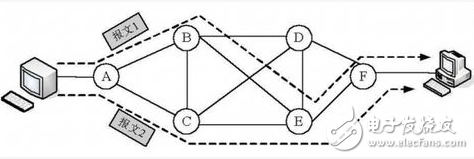
**Packet Switching**
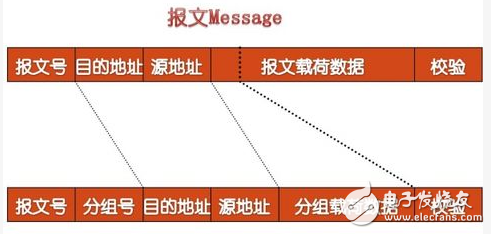
Packet switching also uses the store-and-forward method but divides long messages into smaller packets. Each packet carries the source and destination address along with a sequence number. Compared to message exchange, packet switching has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
**Advantages of Packet Switching**
1. Data transmission is faster because packets can be processed in parallel. While one packet is being forwarded, the next one can be stored, reducing overall transmission time.
2. Fixed-size packets simplify buffer management, making memory handling more efficient.
3. Shorter packets reduce the probability of errors and minimize retransmission, improving reliability and reducing delays.
4. Shorter packets make it easier to implement priority policies, making packet switching ideal for bursty data traffic.
**Disadvantages of Packet Switching**
1. Despite lower delay than message switching, there is still some store-and-forward delay. Switching nodes require more processing power.
2. Adding headers to each packet increases overhead by 5–10%, slightly reducing efficiency and complicating control.
3. With datagram service, packets may arrive out of order, lost, or duplicated, requiring sorting at the destination. Virtual circuits avoid this but add setup and release phases.
Indoor Poster Led Display,Indoor Poster LED digital signage,Indoor Poster LED display show,Floor Standing LED Poster digital signage,LED Mirror Ad Players,Cascade connection Poster LED display
Shenzhen Xinfei Century Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.rgbdancing.com
