Yesterday, I was asked about the "Xiaobian Xiaolong 835's Win instinct" and also wanted to understand the difference between a mobile phone CPU and a computer CPU. This is actually an interesting topic because, unlike in the past, mobile phone CPUs are now moving toward multi-core development, and their computing power has become quite impressive. It's no wonder that many people are discussing this issue. Xiaobian mentioned today that the differences between the two are significant, and even though they're both called CPUs, they're fundamentally quite different.

We Are Not the Same
Although both are referred to as CPUs, they are fundamentally different—mainly in terms of architecture. When we talk about computer CPUs, they are typically based on the X86 or X64 architecture, while modern mobile phone CPUs are built on the ARM architecture. These two architectures were designed with completely different goals in mind, and this also relates to the instruction set used.

The instruction set used by computer CPUs is known as CISC, which stands for "Complex Instruction Set Computer." The CISC instruction set is very rich and includes complex commands, allowing operations to be more targeted and efficient. In contrast, ARM-based CPUs use RISC, or "Reduced Instruction Set Computer," which focuses on optimizing common instructions for a more streamlined execution environment. Less commonly used functions are handled through simplified instructions instead.
In short, computer CPUs (like X86/X64) are better suited for complex environments, while ARM-based mobile CPUs are optimized for specific tasks. Their design philosophies are fundamentally different—one aims for versatility and power, while the other emphasizes efficiency and precision.

So why does the ARM CPU keep improving every year, while computer CPUs seem to progress more slowly? The main reason is that RISC-based CPUs have a simpler structure, a more compact layout, and often a modular design. This makes them easier to update and implement the latest technologies. On the other hand, CISC CPUs have a more complex structure, which leads to longer design cycles, and computers still haven’t fully adopted the modular approach seen in ARM CPUs.

Can They Replace Each Other?
However, as time goes on, ARM-based CPUs have shown incredible flexibility and performance improvements. Some tests even suggest they can rival X86/X64 CPUs. But can they truly replace them? The answer is no. In Xiaobian’s view, ARM CPUs are more likely to act as complements rather than replacements.
For the foreseeable future, the powerful performance of computer CPUs will remain unmatched by mobile ones. This is because computer CPUs are designed to handle a wide range of complex tasks, whereas mobile CPUs are specialized and optimized for specific functions.
For example, mobile phones can decode 4K video without much power consumption due to hardware optimization and specialized algorithms. This means that mobile CPUs can be tailored for key functions, while computer CPUs focus on versatility and broad compatibility.
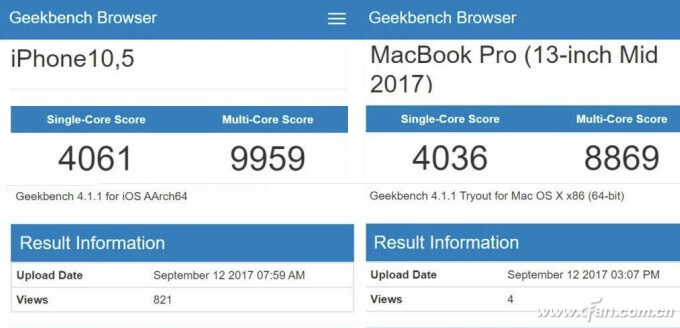
You can see that the Xiao Long 835 notebook supports Windows EXE applications thanks to Microsoft and Qualcomm's collaboration and targeted optimizations. However, the product hasn't been officially released yet, and it's waiting until full simulation compatibility is achieved—meaning the product will only come out when the Xiao Long 845 is ready. Even then, these devices are mainly aimed at ultra-thin and ultra-portable notebooks, and their performance won't match traditional computer CPUs anytime soon.

2.0mm Pitch
2.0mm Pitch
HuiZhou Antenk Electronics Co., LTD , https://www.atkconn.com
