Yesterday, I was asked about the "Xiaobian Xiaolong 835" and its "Win instinct." Also, there's a growing interest in understanding the difference between mobile phone CPUs and computer CPUs. This topic is quite fascinating, especially now that mobile processors are evolving toward multi-core designs with impressive computing power. No wonder people are starting to compare them more closely. Xiaobian explained today that, although they both have the word "CPU," their genetic makeup is still quite different.

We Are Not the Same
Although both are called CPUs, they are fundamentally different—mainly in terms of architecture. When we talk about computer CPUs, they typically use the X86 or X64 architecture, while modern mobile CPUs are based on the ARM architecture. These two architectures were designed with different goals in mind, and this affects the instruction set used by each.

The instruction set used by traditional computer CPUs is known as CISC, which stands for "Complex Instruction Set Computer." CISC has a rich set of complex instructions, allowing operations to be more targeted and efficient. On the other hand, ARM-based CPUs use RISC, or "Reduced Instruction Set Computer," which focuses on optimizing common commands to create a more streamlined execution environment. Less frequently used functions are handled through simplified instructions instead.
In simple terms, computer CPUs (like X86/X64) are better suited for complex environments, while ARM CPUs are optimized for specific tasks. Their design philosophies are different: one aims for versatility and power, while the other emphasizes efficiency and precision.

That’s why ARM CPUs tend to advance quickly every year, while computer CPU improvements seem slower. The reason lies in the RISC architecture's simplicity, compact layout, and modular design, which allows faster development cycles and easier integration of new technologies. In contrast, CISC CPUs have a more complex structure, leading to longer design cycles and less flexibility compared to ARM.

Can They Replace Each Other?
Despite this, ARM-based CPUs are becoming more powerful with each generation, and some even show performance that rivals traditional computer CPUs. However, can they truly replace them? The answer is no. In Xiaobian’s view, ARM CPUs are more likely to complement rather than replace computer CPUs.
For the foreseeable future, computer CPUs will still outperform mobile ones in most demanding tasks. Mobile CPUs are specialized, designed for specific functions, while computer CPUs are built for versatility. For example, a smartphone can decode 4K video efficiently because it uses hardware-optimized algorithms. But a computer CPU must handle a wide range of tasks, making it less efficient in highly specialized areas.
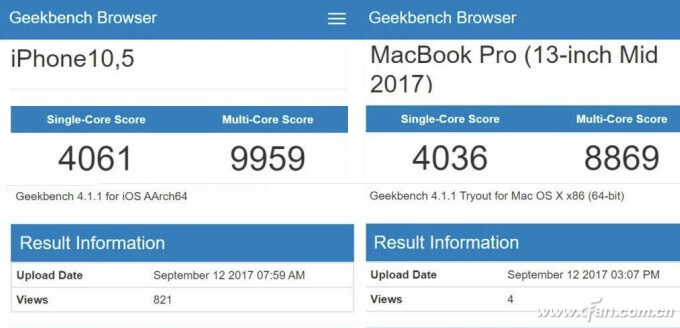
Take the Xiaolong 835, for instance. It supports Windows EXE applications thanks to a collaboration between Microsoft and Qualcomm. However, it hasn’t been widely released yet, as full compatibility needs to be perfected. The product is expected to launch only after the Xiaolong 845, and even then, it will mainly target ultra-thin and portable notebooks. In terms of raw performance, it still lags behind traditional computer CPUs.
So, while mobile CPUs are improving rapidly, they are not yet ready to fully replace computer CPUs. Both have their own strengths and purposes, and the future may see more collaboration than competition between the two.

4.2mm Pitch
4.2mm Pitch
HuiZhou Antenk Electronics Co., LTD , https://www.atkconn.com
